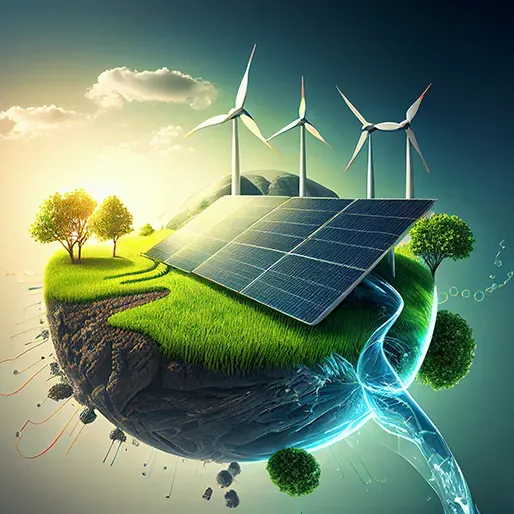
Sustainable Technology is redefining how we design products, power cities, protect ecosystems, and shape a more resilient economy for communities around the world. As a unifying lens for innovation, it champions efficiency, renewable resources, circular thinking, and systems thinking across product design, construction, and mobility. This approach reduces waste, lowers emissions, saves money, and creates new opportunities for startups, established firms, and public services across energy, transport, manufacturing, and infrastructure. By weaving green innovations and low-carbon technology into systems, communities gain resilience, lower utility costs, improved air and water quality, and long-term savings that compound over time. In practice, this approach translates into smarter choices, healthier environments, stronger local economies, and measurable progress for people and the planet.
Viewed through Latent Semantic Indexing principles, you can frame the idea with alternatives like green tech, eco-conscious design, and low-emission solutions that convey the same focus. Additional related phrases—such as circular economy, energy efficiency, sustainable design, and responsible innovation—help map content to varied search intents while expanding the semantic field. Using these substitutes keeps the narrative approachable for readers and signals relevance to search engines without duplicating terms.
Sustainable Technology and Green Innovations: Paving a Low-Carbon Future
Sustainable Technology serves as a practical lens for designing products, cities, and services that minimize environmental impact. By weaving energy efficiency, lifecycle thinking, and circular design into everyday solutions, we advance green innovations that reduce emissions and conserve resources. In this context, low-carbon technology becomes not just a concept but a daily practice—embedded in building materials, transportation systems, and digital infrastructures that power modern life with less carbon intensity.
This approach extends across sectors, from energy and transport to manufacturing and urban planning. When cities deploy sensors to cut energy waste, optimize waste collection, and manage water more effectively, they demonstrate how sustainable technology translates into tangible outcomes. The result is a growing portfolio of green innovations—ranging from smarter appliances to modular, repairable products—that reinforce a resilient, climate-conscious economy.
Renewable Energy Technology and Eco-Friendly Solutions for Everyday Life
At the heart of sustainable progress lies renewable energy technology. Solar PV panels, wind turbines, geothermal systems, and hydropower offer scalable ways to generate electricity with dramatically lower carbon footprints than fossil fuels. Advances in materials science boost panel efficiency and reduce costs, while smart grid technologies and demand response programs balance supply and demand in real time. Storage solutions—from lithium-ion to emerging chemistries—smooth variability and help create a reliable, resilient energy system.
Eco-friendly technology emphasizes products and systems designed to minimize environmental impact throughout their life cycle. From energy-efficient appliances to passive solar and circular design, these solutions lower energy use, curb waste, and promote healthier indoor environments. Embracing recyclable materials, repairability, and take-back programs strengthens brand trust and enables households and businesses to participate in a circular economy that supports long-term sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sustainable technology and how do green innovations and eco-friendly technology contribute to everyday solutions?
Sustainable technology refers to solutions that minimize environmental and social impacts while maximizing benefits for people and ecosystems. It combines energy efficiency, lifecycle thinking, and circular design. Green innovations and eco-friendly technology translate these principles into real products and systems—reducing resource use, lowering emissions, improving indoor air quality, and extending product lifespans in homes, workplaces, and cities.
Why is renewable energy technology central to sustainable technology, and how do low-carbon technology approaches reduce emissions in industry and mobility?
Renewable energy technology, including solar, wind, geothermal, and storage, is central to sustainable technology. It enables clean power, supports smart grids, and lowers reliance on fossil fuels. When paired with low-carbon technology—electrification of transport, energy-efficient manufacturing, and advanced materials—these approaches cut emissions, reduce energy intensity, and create more resilient industry and mobility systems.
| Aspect | Key Points | Examples / Details | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| What is Sustainable Technology? | Minimizes negative environmental and social effects while maximizing positive outcomes; lifecycle thinking; longer product lifespans; repairability; recyclable materials; decouples progress from pollution. | Cities using sensors to cut energy use; durable, repairable products; circular design. | Lower emissions; reduced resource use; extended product lifecycles. |
| Green Innovations | Showcase energy systems and smart devices that lower emissions, save resources, and support healthier communities. | Examples: green energy tech; energy-efficient devices. | Direct emissions reductions; resource conservation. |
| Renewable Energy Technology | Solar PV, wind, geothermal, hydropower; storage; smart grids; demand response. | Reduces carbon footprints vs fossil fuels; resilience. | Lower carbon intensity; flexible supply; grid stability. |
| Eco-friendly Technology in Everyday Life | Energy-efficient appliances; passive solar design; circular design; modular repairable components; materials with minimal ecological footprints. | Lower energy use; better indoor air; longer product lifespans; repairability. | Improved environmental footprint and cost savings. |
| Low-Carbon Technology in Industry and Mobility | Process improvements; electrification of transportation; advanced materials for lighter, stronger products; EVs, hydrogen, efficient hybrids; heat recovery; digital twins; smart HVAC. | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels; energy demand shrinking. | Reduced emissions; energy efficiency gains. |
| Circular Economy & Sustainable Materials | Design for reuse, refurbish at scale, and recycling as standard; bio-based polymers; recycled metals; low-emission concretes; end-of-life take-back and closed-loop recycling. | Durable products; resource recovery; opportunities in repair and remanufacturing. | Conserved resources; reduced waste streams. |
| Water, Agriculture, and Resource Resilience | Water security and healthy food systems; advanced water treatment; energy-recovery desalination; precision agriculture; sensors and data analytics. | Optimized irrigation, fertilizer usage, and crop health; boosted yields. | Improved resilience; reduced environmental impact. |
| Policy, Economics, and Implementation Pathways | Aligned policy signals, financing, and market mechanisms; incentives for clean energy; regulatory sandboxes; procurement policies; workforce development; standards. | Faster adoption; safer, reliable products. | Wider deployment of sustainable technology with accountable outcomes. |
| Case Studies and Real-world Impacts | Campus microgrids; heat-recovery ovens; smart street lighting; real-world deployments reducing emissions and improving reliability. | Demonstrates practicality and benefits of Sustainable Technology. | |
| Challenges and Opportunities on the Horizon | Upfront capital, risk perceptions, and new skill needs; policy support and collaboration required. | Costs fall as technologies mature; scalable recycling and better data enable deployment. | Paves the way for broader adoption and systemic change. |
Summary
Sustainable Technology serves as a practical, inclusive framework for reducing environmental impact while boosting human and ecological well-being. It aligns with renewable energy technology, eco-friendly technology, and low-carbon technology as it scales efficiency, renewables, and circular design across energy, transport, manufacturing, and water systems. By embracing lifecycle thinking, durable design, and smart, data-driven tools, Sustainable Technology helps decarbonize economies and strengthen resilience. The journey relies on coordinated policy, capital, and skilled workforces, and on collaboration among researchers, industry, policymakers, and communities. Across industries and communities, Sustainable Technology translates ideas into tangible benefits: lower emissions, resource conservation, cost savings, and healthier environments. As adoption grows, Sustainable Technology will redefine how products are designed, how cities are powered, and how everyday choices align with planetary boundaries.