Cybersecurity Essentials form the guardrails that individuals, families, and organizations rely on in today’s connected world. As our lives depend on smartphones, laptops, cloud services, and smart devices, understanding digital security best practices helps you limit exposure to cyber threats. A strong foundation in these principles reduces risk, protects data, and supports data protection and online privacy across home, work, and school environments. This guide translates complex concepts into practical steps you can weave into daily routines and small-business processes. By prioritizing identity and access management, device hygiene, and network security, you’ll build a resilient shield against evolving cyber threats.
Viewed through a different lens, this topic aligns with information security fundamentals—the disciplined practices that protect digital assets. It’s a layered approach to safeguarding data, devices, networks, and user privacy across homes and small businesses. Key elements include strong identity verification, regular software upkeep, encryption, and secure network configurations. By framing protection as an ongoing habit rather than a one-time setup, individuals and teams can maintain resilience against emerging threats. In essence, digital defense brings together people, policies, and technology to keep information safe, private, and trustworthy.
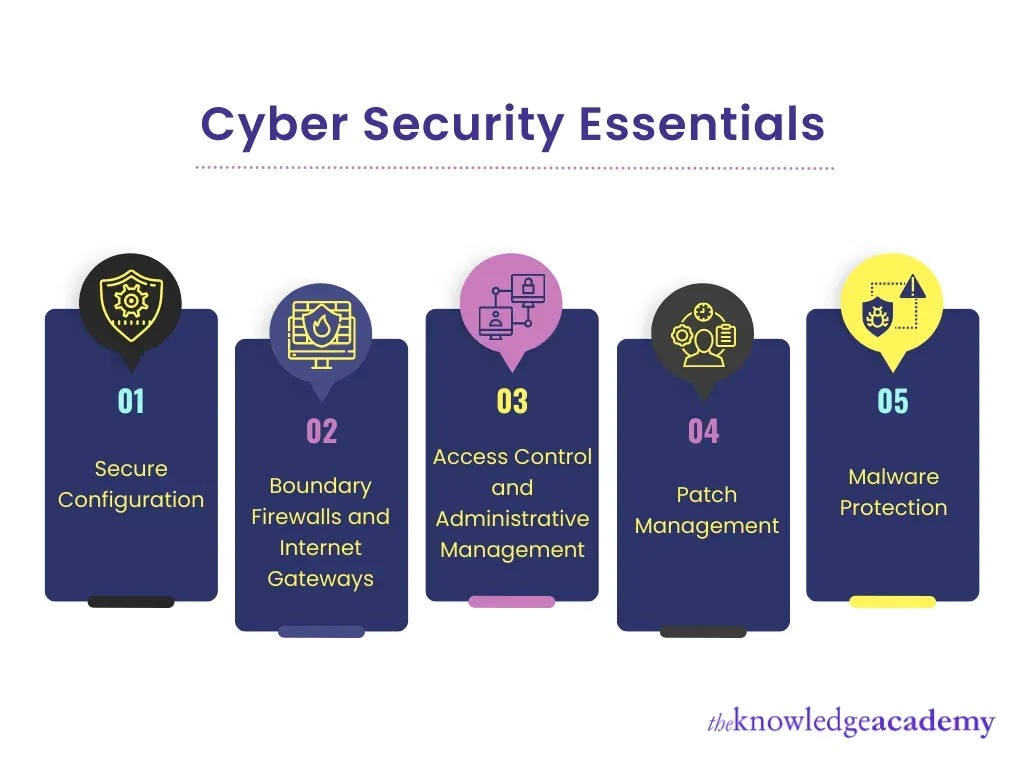
Cybersecurity Essentials: A Practical Framework for Digital Security Best Practices
Cybersecurity Essentials are not optional; they define a layered defense for individuals, families, and organizations. By focusing on identity and access management, device hygiene, data protection, and network security, you create a resilient shield against evolving cyber threats. This approach embodies digital security best practices by reducing exposure and increasing the difficulty for attackers to succeed.
Adopting Cybersecurity Essentials in daily life starts with a baseline: enable MFA, use unique passwords, and keep software up to date. Use a password manager to avoid reuse, and activate automatic updates where possible. Secure data in transit with encryption, implement reliable backups with tested restoration, and stay vigilant against phishing and social engineering. These steps also support online privacy by limiting information leakage.
Strengthening Home and Small-Business Network Security for Online Privacy and Data Protection
Network security is the foundation of a safer digital environment at home and for small teams. Replace default router credentials, deploy a strong Wi‑Fi password, and enable WPA3. Segment networks for guests and IoT devices, keep firmware current, and disable unused services to reduce attack surfaces. This focus helps mitigate cyber threats and ensures data protection in transit.
Beyond the technology, practical habits matter: use a trusted VPN on public networks, avoid risky connections, and monitor for unusual activity. Regular backups and tested restores support data protection goals, while awareness of social engineering reduces susceptibility to phishing. A robust network security posture also preserves online privacy by limiting data exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What practical steps can individuals take to implement Cybersecurity Essentials in daily life to protect online privacy and data protection?
To implement Cybersecurity Essentials in daily life: 1) Identity and access management: enable MFA on critical accounts and use a password manager to create and store unique passwords. 2) Device and software hygiene: enable automatic updates, remove unused apps, and run reputable security scans with active antivirus/endpoint protection. 3) Data protection: enable device encryption, encrypt sensitive files, back up important data to a separate location, and regularly test restores. 4) Network security: change default router credentials, use a strong Wi‑Fi password with WPA3, keep firmware updated, and use a trusted VPN on public networks. 5) Online privacy and phishing awareness: be cautious of unsolicited messages, verify sources before sharing credentials, and avoid risky links. 6) Incident readiness: maintain a simple incident response plan and periodically review backups and permissions.
How do the pillars of Cybersecurity Essentials—identity and access management, device and software hygiene, data protection, and network security—work together to defend against cyber threats?
They form a layered defense against cyber threats. Identity and access management reduces credential abuse through MFA and unique passwords. Device and software hygiene closes vulnerabilities with timely updates and endpoint protection. Data protection safeguards confidentiality and integrity via encryption, backups, and tested restores. Network security protects data in transit with strong Wi‑Fi settings, VPNs, and network segmentation. Together, these pillars lower the attack surface, improve resilience, and reflect digital security best practices that support online privacy and safer technology use.
| Pillar / Topic | What it covers | Practical Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Foundational protections; risk reduction; layered approach to Cybersecurity Essentials | Develop a cybersecurity plan; weave best practices into daily life (individuals, families, and small teams) |
| Identity and Access Management | Strong authentication; unique complex passwords; MFA; password managers; rotate credentials | Enable MFA; use a password manager; rotate credentials regularly |
| Device and Software Hygiene | Regular updates and patches; automatic updates; remove unused software; run scans; keep antivirus updated | Enable automatic updates; schedule restarts; maintain a clean device environment |
| Data Protection and Encryption | Encrypt data at rest and in transit; backups; encryption best practices | Use encryption; full-disk encryption; secure channels (HTTPS, VPN); test backups/restores |
| Network Security and Safe Connectivity | Secure networks; change default router credentials; WPA3; VPN; avoid untrusted networks | Change router credentials; enable WPA3; use VPN; segment networks |
| Putting Cybersecurity Essentials Into Practice | Practical steps for individuals, families, and teams | Baseline security; credential management; data protection; network security; phishing awareness; incident planning |
| The Human Element | People drive effectiveness; education and awareness | Encourage MFA, safe browsing, phishing awareness |
| Common Threats and Mitigations | Phishing, malware/ransomware, unsecured networks, data breaches, IoT vulnerabilities | MFA, updates, VPNs, encryption, segmentation |
| Measuring Progress | Metrics to track improvement | Accounts with MFA; up-to-date software; backups/restores; incidents; user awareness |
| The Bottom Line | A practical framework for protecting technology | Adopt small, consistent steps: MFA, updates, encryption, awareness |
Summary
Cybersecurity Essentials provide a practical, descriptive framework for safeguarding people, data, and devices in today’s interconnected world. By embracing the pillars of identity management, device hygiene, data Protection, and network security, individuals and organizations can reduce risk, preserve privacy, and build lasting trust. The approach is layered and actionable: implement MFA, keep software updated, encrypt sensitive data, secure networks, educate users, and plan for incident response. When these practices become daily habits, Cybersecurity Essentials translate into tangible protection for everyday life, home networks, and small teams navigating the digital landscape.