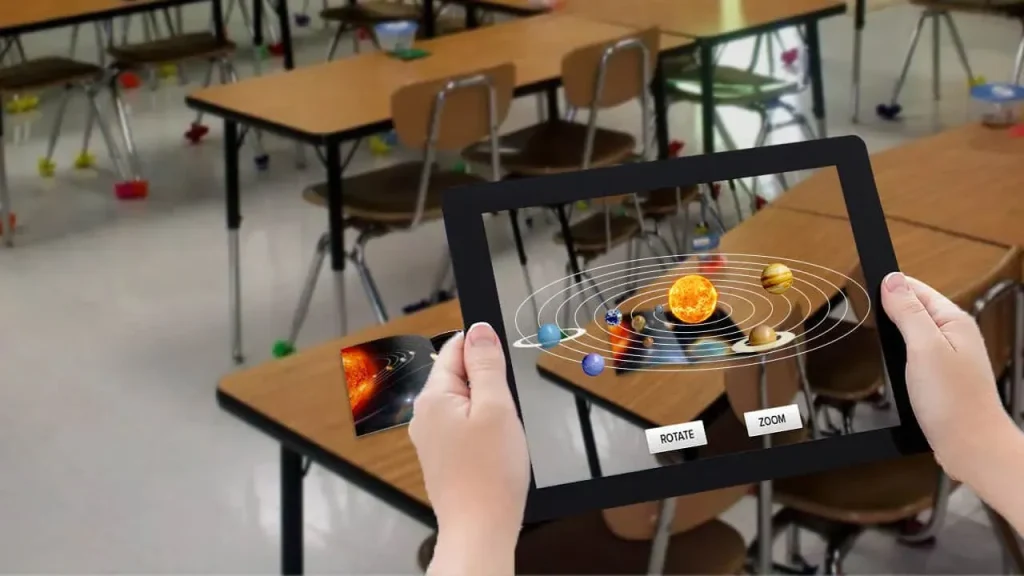
Augmented Reality in Education is transforming how learners see and interact with the world. By overlaying digital information onto real environments, AR creates a bridge between abstract concepts and tangible understanding. In classrooms, AR learning tools turn static lessons into dynamic experiences that boost engagement and retention. Educators can cultivate an immersive learning environment with an augmented reality classroom that supports collaboration and inquiry. This post explores how AR in education can elevate curricula, outlines practical integration steps, and highlights the potential of educational technology with AR.
Beyond the explicit label, this field is often described as AR-enabled pedagogy, where digital overlays enrich classroom practice. Other terms such as mixed reality, augmented overlays, and wearable-assisted learning capture the same core idea of blending simulations with the real world. Educators deploy AR-driven tools to render scientific models, historical reconstructions, and interactive experiments that map neatly to established standards. These approaches support immersive learning, promote inquiry, and help students develop spatial reasoning and data literacy. As schools adopt educational technology with AR and related augmented reality methods, thoughtful design and accessible implementation help ensure benefits reach all learners.
Augmented Reality in Education: Transforming Classrooms with Immersive Learning
Augmented Reality in Education blends digital information with the real world to create immersive learning experiences that make abstract concepts tangible. By overlaying 3D models, animations, and contextual data onto real objects, AR in education fuels curiosity and supports immersive learning across subjects. This approach leverages AR learning tools to turn a math diagram into a manipulable geometric space or bring a biology cell to life, helping students connect theory with hands-on discovery.
To implement AR effectively, educators select AR learning tools that align with standards, ensure accessibility, and provide teacher dashboards for assessment. When integrated into an augmented reality classroom, these tools promote collaboration, scaffold inquiry, and offer immediate feedback, which supports differentiated instruction and strengthens retention through experiential practice. This is a core part of educational technology with AR, enabling schools to scale innovative experiences while preserving learning goals.
AR Learning Tools in the Augmented Reality Classroom: Strategies for Educational Technology with AR
Selecting AR learning tools begins with clarifying learning outcomes and checking that tools support accessibility and device compatibility. In the augmented reality classroom, marker-based or markerless tracking can adapt to different lesson contexts, from anatomy overlays to historical reconstructions. The use of AR learning tools enhances engagement and helps students develop information literacy, collaboration, and observation skills across disciplines.
Beyond tool selection, effective design considers cognitive load, privacy, and ongoing professional development for teachers. A practical strategy is to pilot short AR experiences within a single unit, collect student feedback, and measure learning gains with formative assessments tied to standards. When done thoughtfully, educational technology with AR becomes a scalable driver of immersive learning and evidence-based practice in the classroom.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Augmented Reality in Education, and how do AR learning tools support immersive learning in the augmented reality classroom?
Augmented Reality in Education blends digital content with the real world to enhance lessons. Using AR learning tools, students interact with 3D models and overlays, creating immersive learning experiences in the augmented reality classroom. This approach boosts engagement, supports deeper understanding of complex concepts, and promotes collaboration and exploration across subjects, while maintaining accessibility and adaptability for diverse learners.
What are best practices for implementing Augmented Reality in Education using educational technology with AR, and how can schools scale AR experiences across curricula?
Start with clear learning outcomes and align AR activities to standards. Choose age-appropriate AR learning tools, provide digital literacy and safety guidance, and offer professional development for teachers. Implement a blended model with reliable devices and connectivity, plan for scalable lessons, and use formative assessments to measure impact. Prioritize accessibility and equity, consider offline options, and maintain privacy and data security as AR experiences expand across the curriculum.
| Theme | Key Points | Notes / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| What is AR in Education | AR blends digital content with the real world; overlays 3D models, animations, and contextual data onto real objects or spaces; differs from VR by enhancing reality, not replacing it. | Examples: inspect a 3D cell, manipulate a virtual planet, view historical artifacts in class; AR apps support teaching across subjects. |
| Benefits of AR in Education | Increases engagement; supports deeper understanding via immersive visuals and spatial representations; enables differentiated instruction; promotes collaboration; broadens access to experiences like virtual field trips. | AR helps with complex concepts by showing relationships in 3D space; suitable for diverse learners and contexts. |
| AR Learning Tools and Technologies | Tools run on tablets/phones/classroom devices; marker-based vs markerless tracking; interactive 3D models, real-time annotation, layered data; content customizable; accessible dashboards. | Look for accessibility, alignment with learning objectives, and teacher-friendly assessment features. |
| Use Cases Across Subjects | Science: cell structures, skeletons, chemical simulations; Geography/History: ancient cities, landscapes; Math: geometry, volume, transformations; Language Arts: settings, vocabulary; Cross-disciplinary, experiential learning. | AR enables hands-on exploration and evidence-based reasoning across disciplines. |
| Implementation Strategies for AR in Education | Set clear objectives; pilot AR within a unit before scaling; blend AR with traditional instruction; ensure device access and classroom management; plan for assessment. | 5 key steps: align standards; choose age-appropriate tools; prepare digital literacy/safety; provide professional development; establish assessment methods. |
| Design Considerations and Accessibility | Consider cognitive load; clear objectives and guided prompts; ensure cross-device compatibility; provide captions, audio descriptions, and alternative formats; address privacy and safety. | Prioritize inclusive design so all students can participate. |
| Challenges and Solutions | Device access and connectivity gaps; content quality and pedagogy alignment; added teacher workload. Practical solutions include BYOD/sharing schedules, offline AR options, ready-to-use lesson plans, teacher communities, and ongoing PD. | Choose pedagogy-forward apps; use scalable plans; invest in professional learning communities. |
| Best Practices for Designing AR Experiences | Map AR activities to learning outcomes; concise prompts and guided exploration; integrate AR into the lesson flow; reveal unseen relationships; foster collaboration; include formative assessment prompts; ensure accessibility and equity. | Robust, learner-centered designs that scaffold and assess progress. |
| Future Trends in AR and Education | AR with AI for adaptive, real-time lessons; cross-curricular connections; wearables and efficient hardware; analytics dashboards to measure engagement and outcomes; expanded teacher professional development and AR literacy. | Expect more seamless, personalized AR experiences tied to curriculum. |